The customer is an emerging automotive OEM and a rising player in autonomous systems, focused on developing next-generation vehicle software and AI-driven functionality. Their ADAS platform is built around the TI TDA4VH-Q1, an automotive-grade SoC designed for sensor fusion, L2/L3 domain controllers, and AI/video acceleration. The customer is deploying an L2+ ADAS software stack, with a clear path toward future expansion to Level 3 autonomy.
The challenge: TI’s standard SDKs could not be used as-is due to the customer’s choice of non-standard peripherals, primarily cameras and display. A partner was required to adapt and extend the low-level platform software, providing a stable foundation for ADAS stack deployment.
RT-RK was engaged to provide system-level bring-up, SDK adaptation, and board-level software integration, preparing the platform for the customer’s ADAS stack.
Figure 1. L2+,L3 ADAS features
Project Requirements
RT-RK’s engagement covered the following scope:
- Platform Bring-Up: Full initialization and functional verification of the customer’s hardware platform.
- Base Software and Driver Development: Modification and development of SE and drivers, based on TI PDSK Linux and TI PDSK RTOS frameworks.
- Boot Image Creation: Development and verification of boot images across multiple complex boot flows.
- Design and Development Deliverables: Provision of source code, build environment, and design files (where applicable).
- Testing and Documentation: Comprehensive functional and interface testing, and creation of detailed documentation.
System Architecture
The ADAS system integrates a broad range of sensors and interfaces:
- Cameras: 1 wide FOV front camera for perception, 4 fisheye cameras for surround view, 1 interior NIR camera for Driver Monitoring System (DMS), 6 GMSL2 cameras.
- Radar: 1 long-range front radar, 4 short- and medium-range corner radars.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: 12 total, forming a full surround array.
- Central Computer: Based on TDA4VH-Q1 SoC.
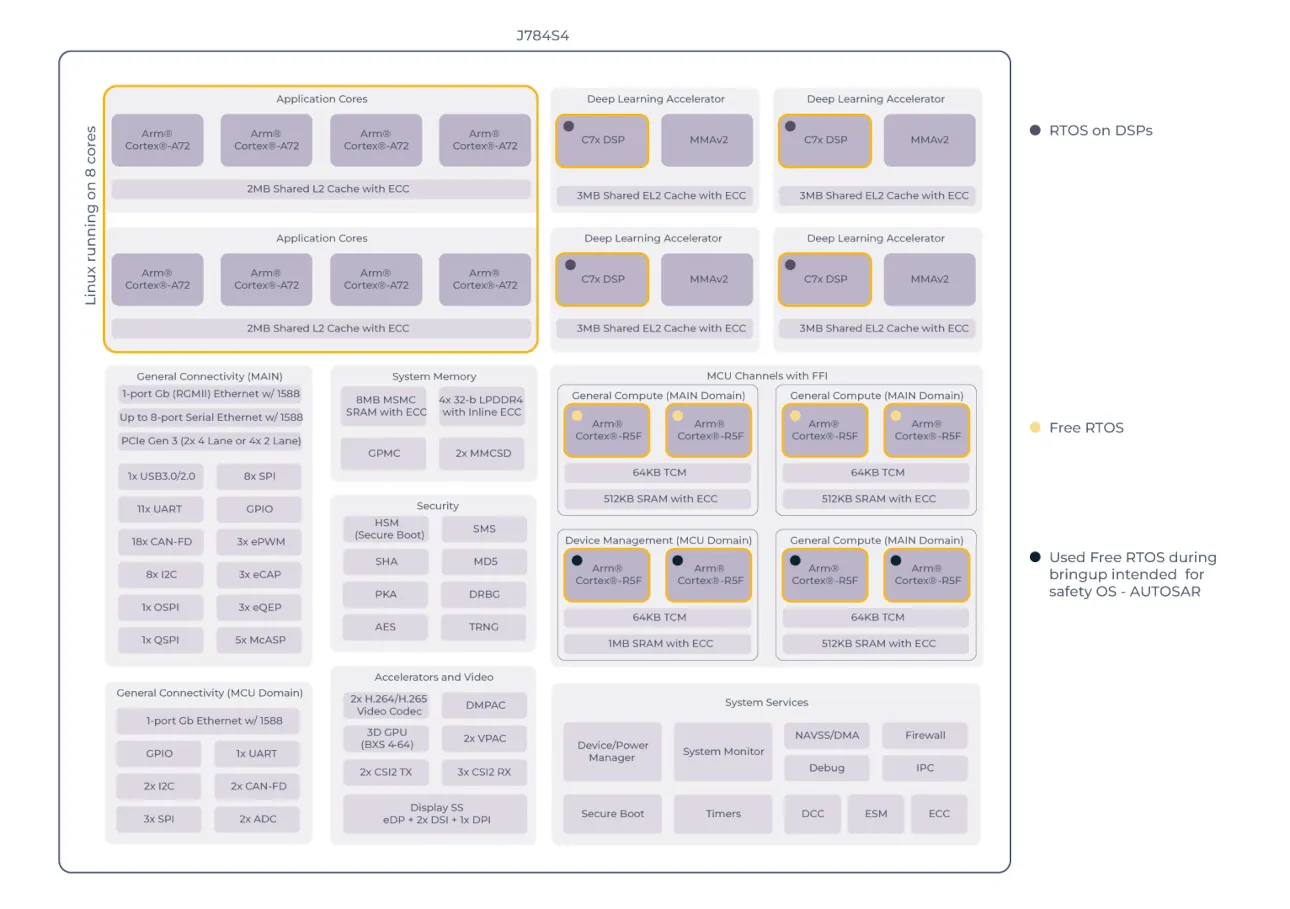
TDA4VH-Q1 Architecture Details
- Linux Domain: 8 × Arm Cortex-A72 cores running general-purpose Linux.
- Deep Learning Accelerators: 4 × C7x DSP cores running RTOS for AI workloads.
- MCU / Safety Domain: 8 × Arm Cortex-RSF cores running FreeRTOS for device management and safety-critical tasks. These cores provide Free-from-Interference (FFI) operation and are intended for AUTOSAR-compliant safety OS tasks.
Technical Complexity Example:
Verifying a CAN bus cannot be done solely from Linux. Proper operation must also be confirmed from RTOS cores, as critical communication may originate from safety domains. This requires careful integration and testing.
Figure 2. Inside TDA4VH-Q1
Workflow and Methodology
- Planning: RT-RK defined a detailed bring-up plan, including test environments, task breakdown, and priorities. The plan was reviewed and approved by the customer.
- Primary Bring-Up: Initial validation included JTAG connectivity, memory integrity checks, and verification of supported boot modes. The platform supports multiple boot configurations, including Normal No-Boot/DevBoot, OSPI, RGMII/Ethernet, I2C, UART, eMMC, USB, as well as MCU-only boot modes (OSPI, Ethernet, I2C, UART).
- Core Interface and OS Verification: Basic interfaces such as I2C and USB were verified for connectivity and communication with multiple peripherals, including USB cameras and mass-storage devices. Linux and RTOS were launched and configured, inter-OS communication was validated, and the TI application development framework was confirmed to be fully functional on the target platform.
- CAN Buses: 5 CAN interfaces (three ADAS-related and two spare ‘vehicle’) were verified from both Linux and RTOS domains, ensuring availability across general-purpose and safety-critical software.
- Ethernet: 2 1 Gb automotive Ethernet interfaces were verified via U-Boot, Linux (kernel drivers), and RTOS. RTOS-side Ethernet drivers were developed from scratch, including MDIO support.
- Cameras and Display: 6 GMSL2 cameras and one GMSL2 display were integrated and verified. As TI provides no out-of-the-box support for GMSL2 camera systems, dedicated driver and software development was required.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: 12 ultrasonic sensors were configured and tested via the DSI3 interface. Verification included SPI communication, GPIO-based interrupt handling - through basic hardware/BSP checks to confirm reliable communication.
- Supervision Components: System supervision elements, including watchdogs, temperature sensors, and RTC, were verified across both Linux and RTOS domains.
- Memory Testing: All supported memory types were validated, with initial verification performed in relevant boot modes to ensure correct loading of software images from memory.
After RT-RK’s platform iteration, the customer conducted their ADAS stack validation.
Figure 3. From bring-up to an ADAS ready platform
Why RT-RK
This project required extending the TI SDK beyond out-of-the-box capabilities, particularly to support non-predefined peripherals. RT-RK’s deep experience with TI platforms made it a natural choice. Some of the relevant past projects included:
- ALPHA Automotive Machine Vision reference board (TDA2X)
- TDA2P coprocessor integration for PC-based RAW-to-YUV converters
- Multi-SoC load balancing demonstrator for deep learning algorithms
- FotoNation Driver Monitoring System optimization (TDA3X)
- DENSO video logger development (TDA2P)
Key Benefits Delivered
- Early Project Start: In-house TI evaluation boards and development environment enabled work to start before the customer’s platform was ready.
- Test Applications: RT-RK developed and adapted test software early, reducing overall project risk.
- Rapid GMSL2 Integration: Quick resolution of camera and display interface challenges enabled through continuous collaboration and direct communication with TI.
- Expert Hardware Support: RT-RK’s experienced hardware team provided on-demand debugging, consultation, and rapid fixes.
Conclusion
RT-RK successfully delivered a fully operational platform for the customer’s TDA4VH-Q1 ADAS system, enabling reliable integration of custom peripherals and establishing a solid foundation for the L2+ software stack. Leveraging deep TI expertise, advanced platform bring-up experience, and agile problem-solving, the team completed the project efficiently, providing robust documentation and test results that allowed the customer to focus on their core ADAS software development.